Metacarpophalangeal fractures are a common fracture in hand trauma, accounting for approximately 1/4 of all hand trauma patients. due to the delicate and complex structure of the hand and its fine motor function, the management of hand fractures is far more important and technically complex than the treatment of other long tubular fractures.
Ensuring the stability of the fracture after repositioning is the key to the success of metacarpophalangeal fracture treatment. In order to restore the function of the hand, the fracture often requires proper fixation, and in the past, external fixation with plaster or internal fixation with Kirschner pins was commonly used, but often due to inaccurate fixation or long fixation time, which is not conducive to early postoperative joint rehabilitation, and has a greater impact on the functional recovery of the metacarpophalangeal joint, bringing some difficulties to the functional rehabilitation of the hand.
Modern treatment methods increasingly use stronger internal fixation, such as micro plate screw fixation.
Treatment Principles
The principles of treatment for metacarpal and phalangeal fractures of the hand are: anatomic repositioning, light and firm fixation, early mobility and functional exercise. The principles of treatment for intra-articular and periarticular fractures of the hand are the same as those for other intra-articular fractures: restoration of the anatomy of the articular surface and early functional activity. Treatment of metacarpal and phalangeal fractures of the hand should strive to achieve anatomic repositioning without rotation, lateral angulation, or angular displacement >10° to the dorsal aspect of the palm. If the fracture end of the metacarpal is rotated or displaced laterally at an angle, it will change the normal trajectory of the flexion and extension movement of the finger, causing it to push or fall from the adjacent finger during flexion, affecting the accuracy of the finger function; while an angular displacement >10° to the dorsum of the palm will destroy the smooth contact surface of the bone and tendon, increasing the resistance and range of motion of the tendon in flexion and extension, and causing chronic injury to the tendon, inducing the risk of tendon rupture. risk of tendon rupture.
The metacarpal and phalangeal fractures are similar in their ability to tolerate rotational deformity, while the metacarpal tolerates shortening displacement and dorsal angular displacement better than the phalangeal. The carpometacarpal and metacarpophalangeal joints can compensate for the angular deformity of the metacarpal, and the annular little finger is better adapted to the angular deformity of the metacarpal than the index middle finger. Reduced grip strength due to intrinsic hand muscle shortening is evident only when the metacarpal is angled more than 30° to the dorsal side.
Surgical Approach
The surgical approach for metacarpal fractures is relatively simple and generally uses a dorsal approach, as shown in Figure 4-14. The second metacarpal is incised radially while the fifth metacarpal is incised ulnarly, and the third and fourth metacarpals are often incised medially. If two adjacent metacarpals are operated on at the same time, a median S-shaped incision is used to take into account both surgical sites.
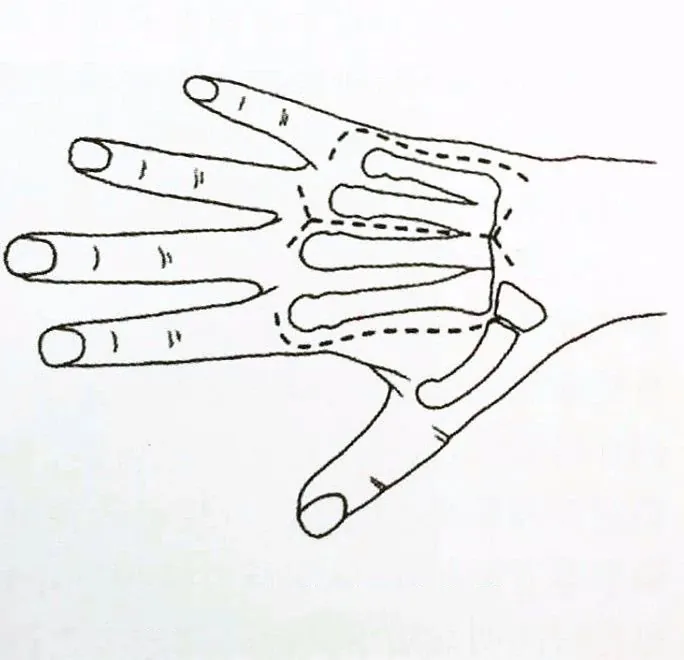
Fixed method selection
There are many internal fixation materials for metacarpophalangeal fractures, such as Kirschner pins, screws, plates and external fixation frames, among which Kirschner pins and microplates are most commonly used. For metacarpal fractures, internal fixation with microplate has obvious advantages over fixation with Kirschner pins and can be preferred; for proximal phalangeal fractures, microplate is generally preferred, but when there is difficulty in placing screws in the distal segment of the proximal phalangeal and head fractures, internal fixation with crossed Kirschner pins is preferred, which is more conducive to the functional recovery of the affected finger; for the treatment of middle phalangeal fractures, Kirschner pins should be preferred.
1、Kirschner's needle:
Kirschner's needle internal fixation has been applied in the clinic for more than 70 years and has been the most commonly used internal fixation material for metacarpophalangeal fractures, which is easy to operate, economical and practical, and is the most classic internal fixation method, as shown in Figure 4-15. as the most commonly used internal fixation for treating hand fractures, it is still widely used.
The advantages of internal fixation with Kirschner pins:
① easy to operate and very flexible in use;
② less soft tissue stripping, less impact on blood flow at the fracture end, less surgical trauma, and favorable to fracture healing;
③ easy secondary pin retrieval;
④ low cost and wide application, applicable to most hand fractures (such as intra-articular fractures, severe comminuted fractures and end phalangeal fractures).
Disadvantages of internal fixation:
(1) compared with plate fixation, the stability is poor, and the shortening and rotational displacement cannot be controlled by a single pin, usually more than 2 pins are needed for cross fixation;
(2) there is no compression effect on the fracture end;
(3) the joint surface is damaged by cross-joint fixation;
(4) the fixation of the joint and the blockage of the tendon prevent the hand joint from early exercise and affect the functional recovery.
With the rapid development of modern internal fixation techniques and equipment, internal fixation with Kirschner pins has become more and more refined, and most of them can be fixed without crossing the joint, with little damage to the soft tissues and tendons around the joint, and without affecting the early postoperative joint function training. With the help of C-arm X-ray machine, some cases can also achieve satisfactory results by closed reduction of internal fixation with Clinique pins, further reducing the damage to local soft tissues and the impact on the blood supply to the fracture end, thus promoting the healing of the fracture.
Precautions for internal fixation with Kristen pins:
① Fix larger bone blocks with Kristen pins of 1.0~1.2 mm in diameter, and determine the point of entry and the direction of entry according to the direction of the fracture line;
② With the aim of restoring the force line, intra-articular fractures must be anatomically repositioned and strongly fixed;
③ Not all bone blocks need to be fixed with Kristen pins, and under the premise of achieving stability of the fracture end, Kristen pins should be used as little as possible;
④ Kristen pins do not fixed through the tendon or dorsal tendon membrane of the finger to create early functional exercise as much as possible;
⑤ there should be a strict preoperative plan and not to repeat the operation intraoperatively, otherwise the fracture block may be more crushed or even unfixable;
⑥ generally the Kirschner pin should be placed in the skin to reduce the chance of infection and it is not difficult to remove it.
![Clinique needle]()
2、Metacarpal micro plate:
Strong internal fixation of hand fractures is the basis for early functional exercise and is necessary to restore good hand function.AO internal fixation technique requires precise anatomical repositioning of the fracture end and stabilization of the fracture end in a functional state, which is commonly referred to as strong fixation, in order to allow early active movement.AO also emphasizes minimally invasive surgical operations, which focus on protecting blood flow. AO also emphasizes minimally invasive surgical procedures that focus on preserving blood flow. Microplate internal fixation of the hand fracture provides satisfactory results in terms of strength, stability of the fracture end and pressure between the ends. In terms of postoperative functional recovery, fracture healing time and infection rate compared, the efficacy of micro titanium plates is considered significantly better than that of kerf pins, and because the fracture healing time after micro titanium plate fixation is significantly shorter than that of other fixation modalities, thus facilitating the early return to normal life of the patient.
Advantages of microplate internal fixation treatment:
(1) compared with kerf pins, microplate screws have better histocompatibility and tissue response;
(2) the stability of the plate nail fixation system and the pressure on the fracture end make the fracture closer to anatomical repositioning, more secure fixation, which is conducive to fracture healing;
(3) early functional exercise is generally allowed after microplate fixation, which is conducive to the recovery of hand function.
![Metacarpal micro plate]()
3. Microscrews.
Microscrews for spiral or long oblique fracture fixation have similar stability as steel plates, but the soft tissue and periosteal stripping area is smaller than that of steel plate fixation, which is conducive to the protection of blood flow and in line with the concept of minimally invasive operation. Although there are T- and L-type splints for proximal joint fractures, the postoperative return visit is poorer than that for diaphyseal fractures, and microscrews have some advantages for intra- and periarticular fracture fixation. Screws screwed into the bone cortex can withstand greater stress load, so the fixation is firm and can put pressure between the fracture ends to bring the fracture surfaces into close contact, which shortens the healing time and facilitates fracture healing, as shown in Figure 4-18. microscrews are mainly used for oblique or spiral fractures of the diaphysis and intra-articular avulsion fractures of larger bone masses. It is important to note that the length of the fracture thread should be at least twice the diameter of the diaphysis when fixing oblique or spiral fractures of the hand stem using microscrews alone, and at least three times the width of the thread diameter when fixing intra-articular avulsion fracture blocks.
![Miniature Screws]()
4. Miniature external fixation brace.
Comminuted metacarpophalangeal fractures are sometimes difficult to reset anatomically even with surgical incision or cannot be strongly fixed internally because the bone scaffold is destroyed. The external fixation brace allows the comminuted fracture to recover and maintain its length under the effect of traction, playing a relatively fixed role, as shown in Figure 4-19. The placement of the external fixation brace differs for different metacarpals: the 1st and 2nd metacarpals are placed on the dorsal radial side, the 4th and 5th metacarpals are placed on the dorsal ulnar side, and the 3rd metacarpal is placed on the dorsal radial or dorsal ulnar side according to the situation, paying attention to the entry point to prevent injury to the tendon. Closed fractures can be closed and repositioned under X-ray, and small incisions can be made to assist in repositioning if the repositioning is not ideal.
![External fixing bracket]()
Advantages of external fixation brace.
(1) it is simple to operate and can adjust various displacements of the fracture end;
(2) it can effectively reset and fix intra-articular fractures of the metacarpal phalanges without damaging the articular surface, and can distract the articular surface to prevent contracture of the joint capsule and lateral collateral ligaments;
(3) it can be combined with limited internal fixation for comminuted fractures that cannot be anatomically reset, and the external fixation brace can partially reset and maintain the force line;
(4) it allows early functional exercises of the affected finger in the unfixed joint to avoid joint
(5) It can effectively fix the hand fracture without affecting the postoperative treatment of the wound of the affected hand.
How to Buy Orthopaedic Implants and Orthopaedic Instruments?
For CZMEDITECH, we have a very complete product line of orthopedic surgery implants and corresponding instruments, the products including spine implants, intramedullary nails, trauma plate, locking plate, cranial-maxillofacial, prosthesis, power tools, external fixators, arthroscopy, veterinary care and their supporting instrument sets.
In addition, we are committed to continuously developing new products and expanding product lines, so as to meet the surgical needs of more doctors and patients, and also make our company more competitive in the whole global orthopedic implants and instruments industry.
We export worldwide, so you can contact us at email address song@orthopedic-china.com for a free quote, or send a message on WhatsApp for a quick response +86-18112515727.
If want to know more information,click CZMEDITECH to find more details.
English
Français
Русский
Español
العربية
Português
Deutsch
italiano
日本語
한국어
Nederlands
Tiếng Việt
ไทย
Polski
Türkçe
አማርኛ
ພາສາລາວ
ភាសាខ្មែរ
Bahasa Melayu
ဗမာစာ
தமிழ்
Filipino
Bahasa Indonesia
magyar
Română
Čeština
Монгол
қазақ
Српски
हिन्दी
فارسی
Kiswahili
Slovenčina
Slovenščina
Norsk
Svenska
українська
Ελληνικά
Suomi
Հայերեն
עברית
Latine
Dansk
اردو
Shqip
বাংলা
Hrvatski
Afrikaans
Gaeilge
Eesti keel
Māori
नेपाली
Oʻzbekcha
latviešu
অসমীয়া
Aymara
Azərbaycan dili
Bamanankan
Euskara
Беларуская мова
भोजपुरी
Bosanski
Български
Català
Cebuano
Corsu
ދިވެހި
डोग्रिड ने दी
Esperanto
Eʋegbe
Frysk
Galego
ქართული
guarani
ગુજરાતી
Kreyòl ayisyen
Hausa
ʻŌlelo Hawaiʻi
Hmoob
íslenska
Igbo
Ilocano
Basa Jawa
ಕನ್ನಡ
Kinyarwanda
गोंगेन हें नांव
Krio we dɛn kɔl Krio
Kurdî
Kurdî
Кыргызча
Lingala
Lietuvių
Oluganda
Lëtzebuergesch
Македонски
मैथिली
Malagasy
മലയാളം
Malti
मराठी
ꯃꯦꯇꯥꯏ (ꯃꯅꯤꯄꯨꯔꯤ) ꯴.
Mizo tawng
Chichewa
ଓଡ଼ିଆ
Afaan Oromoo
پښتو
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ
Runasimi
Gagana Samoa
संस्कृत
Gaelo Albannach
Sepeti
Sesotho
chiShona
سنڌي
Soomaali
Basa Sunda
Wikang Tagalog
Тоҷикӣ
Татарча
తెలుగు
ትግንያውያን
Xitsonga
Türkmençe
संस्कृत
ئۇيغۇرچە
Cymraeg
isiXhosa
ייִדיש
Yorùbá
isiZulu















