The Humeral Nail: An Overview of Surgical Treatment for Proximal Humerus Fractures
Introduction
Proximal humerus fractures are common in the elderly population and can result in significant morbidity and mortality. Surgical management is often necessary for displaced or unstable fractures, and the humeral nail is a widely used treatment option. This article provides an overview of humeral nail surgery, including indications, techniques, and outcomes.
Anatomy of the Proximal Humerus
The proximal humerus consists of the humeral head, greater and lesser tuberosities, and the shaft. The humeral head articulates with the glenoid fossa of the scapula to form the glenohumeral joint, which allows for shoulder motion. The greater and lesser tuberosities provide attachment for the rotator cuff muscles, which are important for shoulder stability.
Proximal Humerus Fractures
Proximal humerus fractures are typically classified based on the location and degree of displacement. Non-displaced fractures can often be managed conservatively with sling immobilization and early range of motion exercises. However, displaced fractures may require surgical intervention to restore shoulder function and prevent complications such as avascular necrosis and non-union.
Surgical Options for Proximal Humerus Fractures
Several surgical options exist for the management of proximal humerus fractures, including open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF), hemiarthroplasty, and reverse shoulder arthroplasty. The choice of surgical technique depends on various factors, including patient age, fracture location, degree of displacement, and comorbidities.
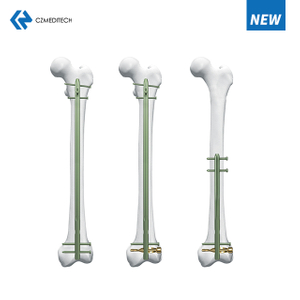
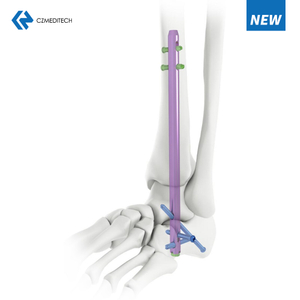
Humeral Nail Surgery
Humeral nail surgery involves the insertion of a long, intramedullary nail through the proximal humerus to stabilize the fracture. The nail is inserted through a small incision near the shoulder joint and is guided into the medullary canal using fluoroscopic guidance. Once the nail is in place, screws are inserted through the nail and into the humeral head to secure the fracture.
Indications for Humeral Nail Surgery
Humeral nail surgery is indicated for displaced or unstable proximal humerus fractures that cannot be managed conservatively. This includes fractures with greater than 1 cm of displacement or fractures with a fracture angle greater than 45 degrees. Humeral nail surgery may also be indicated for patients who are unable to tolerate more invasive surgical procedures, such as hemiarthroplasty or reverse shoulder arthroplasty.
Techniques for Humeral Nail Surgery
Humeral nail surgery can be performed using either a antegrade or retrograde approach. The antegrade approach involves inserting the nail through the proximal end of the humerus, while the retrograde approach involves inserting the nail through the distal end of the humerus. The choice of approach depends on the fracture location and surgeon preference.
Outcomes of Humeral Nail Surgery
Humeral nail surgery has been shown to be an effective treatment option for proximal humerus fractures, with high rates of fracture union and good functional outcomes. However, complications such as screw cutout, non-union, and infection can occur. Careful patient selection and surgical technique are important for minimizing these complications.
Conclusion
Proximal humerus fractures can have significant impacts on patient morbidity and mortality, particularly in the elderly population. Humeral nail surgery is a widely used treatment option that can effectively restore shoulder function and prevent complications. Careful patient selection and surgical technique are important for optimizing outcomes and minimizing complications.
FAQs
How long does it take to recover from humeral nail surgery? Recovery time varies depending on the patient's age and overall health, as well as the severity of the fracture. In general, patients can expect to wear a sling for several weeks following surgery and may need several months of physical therapy to fully regain shoulder function.
Are there any risks associated with humeral nail surgery? As with any surgical procedure, there are risks associated with humeral nail surgery. These can include infection, nerve injury, and blood vessel damage. Additionally, there is a risk of complications such as screw cutout, non-union, and implant failure.
How is patient selection for humeral nail surgery determined? Patient selection for humeral nail surgery is determined based on several factors, including the patient's age and overall health, the severity and location of the fracture, and the presence of any comorbidities that may affect surgical outcomes.
Can humeral nail surgery be used for all proximal humerus fractures? No, humeral nail surgery is typically reserved for displaced or unstable fractures that cannot be managed conservatively. Fractures with minimal displacement or those that do not involve the humeral head may be managed with conservative measures such as sling immobilization and early range of motion exercises.
How long does the humeral nail typically stay in place? The humeral nail is typically left in place for several months to allow for fracture healing. The length of time the nail remains in place may vary depending on the severity of the fracture and the patient's individual healing process.
සිංහල
English
Français
Русский
Español
العربية
Português
Deutsch
italiano
한국어
Tiếng Việt
ไทย
Polski
Türkçe
ພາສາລາວ
ភាសាខ្មែរ
Bahasa Melayu
ဗမာစာ
Filipino
Bahasa Indonesia
magyar
Română
Čeština
Монгол
қазақ
Српски
हिन्दी
فارسی
Kiswahili
Slovenčina
Slovenščina
українська
Ελληνικά
Latine
বাংলা
Afrikaans
Māori
नेपाली
Oʻzbekcha
latviešu
Azərbaycan dili
Беларуская мова
Български
Esperanto
ქართული
Kreyòl ayisyen
Kinyarwanda
Кыргызча
Lietuvių
Lëtzebuergesch
Malti
संस्कृत
Soomaali
Türkmençe
ئۇيغۇرچە