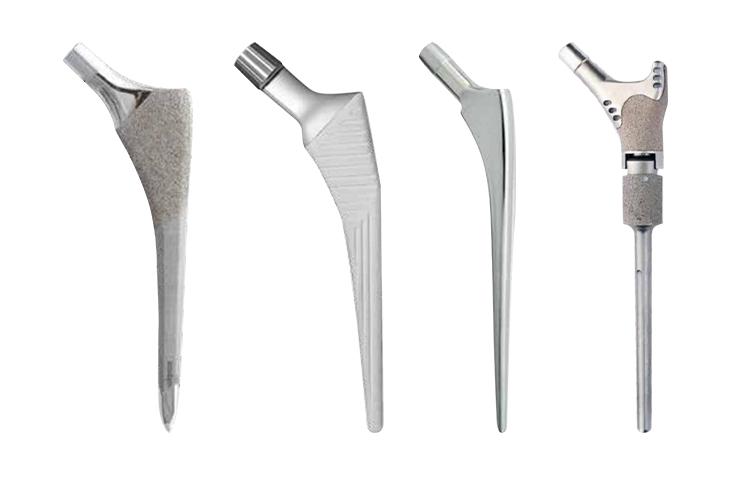
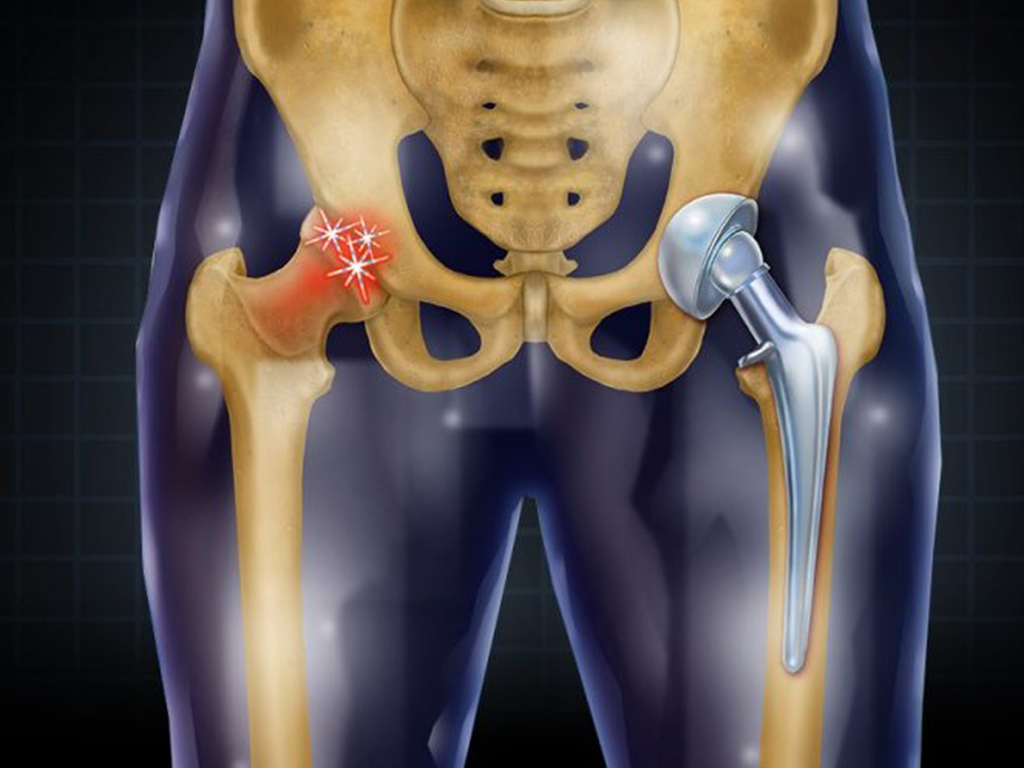
1.What is the femoral stalk
Introduction:
The femoral stem (Femoral Stem) is a part of the metal component used to replace the upper part of the patient's femur (thigh bone) in artificial hip replacement surgery. It is one of the most important components of the artificial hip system and is responsible for connecting to the femoral head and taking on the loads and movements of the hip joint. The main role of the femoral stem is to transfer the movement of the hip joint and the lower limb to the rest of the artificial hip joint, ensuring that the joint is stable, comfortable and functions properly.
Structure and function of the femoral stem
Shape:
The femoral stem is usually tapered or cylindrical and is designed to match the anatomical shape of the human femur. It restores the function of the hip joint by being implanted in the femur and connecting to the femoral head (the other part of the artificial hip joint).
Role:
The femoral stem carries the majority of the body's upper body weight, so it needs to have a strong load-bearing capacity and stability. It must also be biocompatible to ensure osseointegration during long-term use.
Types and designs of femoral stems
![Types of femoral stem Types of femoral stem]()
There are various types of femoral shanks and the common ones include:
Round shank:
Suitable for patients with a nearly round femoral anatomy, it is easier to install, but may not be securely fastened in some patients with osteoporosis.
In addition, the advantages of round shanks include simple surgical procedures and relatively short implantation times. However, it should be noted that in patients with low bone mineral density or osteoporosis, other more suitable femoral stem types may need to be considered to ensure long-term stability.
Tapered shank:
Adjustable shanks:
Progressive shanks:
Femoral shanks with coatings:
Such as cemented or cementless (i.e., osseointegrated), depending on the patient's bone quality and femoral structure. The cemented version is suitable for older patients, while the osseointegrated version is suitable for patients with better bone quality.
The design of the femoral stem commonly includes:
Consideration of anatomical adaptations, such as the angle, length, and curvature of the femoral stem. The choice is made to ensure that the femoral stem makes good contact with the femur and remains stable.
Adjustable design: Some femoral stems are designed with adjustable features that allow for certain adjustments to be made during surgery to adapt them to different anatomical structures.
2.The difference between the different materials of the femoral stem
![股骨柄类型图 股骨柄类型图]()
2.1. Titanium Alloy (Titanium Alloy)
Characteristics:
Titanium alloy is one of the most commonly used materials for femoral stems at present, due to its advantages of good biocompatibility, light weight and strong corrosion resistance. The modulus of elasticity of titanium alloy is close to that of human bone, which reduces the stress concentration between the femoral stem and the bone after implantation and reduces the risk of fracture.
Advantages:
Highly biocompatible and less likely to cause an immune response.
Lighter, helping to reduce the burden after surgery.
High corrosion resistance, suitable for long-term implantation.
Disadvantages:
2.2. Cobalt-Chromium Alloy
Features:
Cobalt-Chromium Alloy is a very strong metallic material and is commonly used for artificial joint components that are required to withstand higher loads. It has better wear and corrosion resistance and provides very high strength and durability.
Pros:
Very strong, suitable for patients with high loads and able to hold weight stably for long periods of time.
High corrosion resistance, suitable for long-term implantation.
High abrasion resistance, capable of reducing wear and tear.
Disadvantages:
Slightly less biocompatible than titanium alloys, may cause minor discomfort in some patients.
Heavier than titanium alloys, which may increase the burden on the patient after surgery.
2.3. Stainless steel (Stainless Steel)
Features:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Stainless steel may cause more significant immune reactions or corrosion problems due to its poor biocompatibility.
Poor corrosion resistance compared to titanium alloys and may be risky for long term use.
2.4. Chromium-Cobalt Alloy (Chromium-Cobalt Alloy)
Characteristics:
This material consists mainly of the elements chromium and cobalt and has high strength and wear resistance. Similar to cobalt-chromium alloys, chrome-cobalt alloys are commonly used in femoral shanks that are subjected to high loads.
Pros:
Extremely strong and wear-resistant, able to withstand high loads for long periods of time.
Extremely resistant to corrosion and suitable for long-term use.
Disadvantages:
Relatively poor biocompatibility, may cause allergic reactions.
Higher weight, may cause discomfort for some patients.
2.5. Ceramic
Features:
Advantages:
High hardness, extremely wear-resistant, reduces friction on the joint surfaces.
Extremely low coefficient of friction reduces wear and long-term fractures.
Disadvantages:
2.6. Surface coating materials (e.g. HA coating, titanium nitride, etc.)
Characteristics:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Coatings may wear off over time, reducing their effectiveness.
Some coatings may increase the complexity and cost of the procedure.
Recommendations:
The choice of material for the femoral stem depends largely on the individual patient (e.g., bone quality, age, activity level, etc.), the type of surgery, the design requirements, and the experience of the surgeon. Titanium alloys and cobalt chromium alloys are the most widely used materials because of their superior strength, durability, and biocompatibility. Certain patients with high loads may prefer cobalt chromium alloy materials, while titanium may be a better choice for younger patients with better bone quality. Regardless of the material, the quality of the design and the ability of the bone to integrate after surgery are key to ensuring stability of the femoral stem and restoration of hip function.
3.What conditions would use the femoral stem
![Where to use the femoral handle Where to use the femoral handle]()
3.1. Osteoarthritis of the hip (Osteoarthritis)
Situation Description:
This is the most common scenario in which the femoral stem is used. The patient's hip cartilage deteriorates, resulting in joint pain, limited movement, and dyskinesia. As the condition progresses, the surfaces of the femur and acetabulum are subjected to severe wear and tear, resulting in a significant loss of joint function.
Purpose of Surgery:
Through artificial hip replacement surgery, the femoral stem is used to replace the damaged part of the femur, thus restoring the function of the hip joint, relieving pain, and improving the patient's quality of life.
3.2. Femoral head necrosis (Avascular Necrosis, AVN)
Situation Description:
Femoral head necrosis is the death of bone tissue in the femoral head due to interruption of the blood supply. This usually results in severe joint pain and loss of function. Necrosis of the femoral head can be caused by a variety of reasons, such as long-term use of steroid medications, trauma, and alcohol abuse.
Surgical Purpose:
When femoral head necrosis cannot be recovered through conservative treatment, artificial hip replacement surgery becomes the treatment option. The femoral stem is used to replace the necrotic part of the femoral head and restore joint function.
3.3. Femoral Fracture
Situation Description:
Especially in elderly patients, femoral neck fractures or femoral stem fractures are common hip fractures. In particular, femoral neck fractures may require artificial hip replacement if the fracture fails to heal or if there are problems such as osteoporosis.
Surgical Objective:
To replace the damaged portion of the femur through femoral stem placement in order to restore the patient's hip function, reduce pain, and improve mobility. The femoral stem is a necessary option for patients with more complex fractures or difficult recovery.
3.4. Hip Joint Infection (HJI)
Situation Description:
In some cases, the hip joint may suffer joint damage due to a bacterial infection, particularly secondary to an infection that occurs after hip surgery (e.g. hip prosthesis infection). This infection can lead to severe damage to soft tissue and bone, or even complete loss of joint function.
Surgical Purpose:
After the infection has been controlled, an artificial hip replacement may be required to restore joint function. In this case, the femoral stem will be used to replace the damaged or infected part of the femur.
![Scenarios for use of the femoral stem Scenarios for use of the femoral stem]()
3.5. Hip Deformity or Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH)
Situation Description:
Some patients may be born with developmental dysplasia of the hip (e.g., hip dislocation or acetabular asymmetry), and these deformities can lead to poor contact between the femur and the acetabulum, resulting in early degeneration of the joint, pain, or dysfunction.
Surgical Objectives:
In cases of developmental hip dislocation or other hip deformities that severely affect quality of life, artificial hip replacement surgery may be required, in which the femoral stem is used to replace the damaged portion of the femur and restore joint function.
3.6. Rheumatoid Arthritis (Rheumatoid Arthritis)
Situation Description:
Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic immune disease that often leads to chronic inflammation and cartilage damage in the joints. When the hip is affected, movement of the joint is limited and pain and dysfunction progressively worsen.
Surgical Purpose:
Artificial hip replacement is an effective treatment for severe damage to the hip joint caused by rheumatoid arthritis. The femoral stem is used in surgery to replace the damaged portion of the femur, thereby reducing pain and restoring joint mobility.
3.7 Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis (SCFE)
Situation Description:
Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis (SCFE) usually occurs during adolescent growth and development, especially during puberty, and may result in misalignment or slippage between the femoral head and the femoral stem. This condition, if left untreated, may lead to joint degeneration or loss of function.
Surgical Purpose:
In some cases, slipped femoral heads cannot be recovered with conservative treatment and may require artificial hip replacement surgery. A femoral stem can be used to replace the damaged part of the femur and restore normal joint function.
3.8. Revision or Replacement after Hip Arthroplasty (Revision Hip Arthroplasty)
Situation Description:
Artificial hip replacement surgery can be very successful, but over time the prosthesis may wear out, loosen, or fail, resulting in loss of joint function or persistent pain. Hip repair or replacement surgery may be necessary at this point.
Purpose of Surgery:
During a repair or replacement surgery, the femoral stem may need to be replaced or realigned to accommodate the patient's new needs. Often, the femoral stem will be selected with a new design or material based on the wear and looseness of the prosthesis.
![Hip necrosis process Hip necrosis process]()
4.How to choose a brand
4.1. Stryker (Stryker)
![史赛克 史赛克]()
Brief introduction:
Stryker is one of the world's leading medical device companies, offering a range of high-quality orthopaedic implants, particularly in the field of artificial hip joints. Stryker's femoral stems are innovatively designed with a wide range of options for different clinical needs.
Features:
Leading technology, long-term stability, extensive clinical applications and validation.
4.2. Elbo (Zimmer Biomet)
![爱尔博 爱尔博]()
Profile:
Zimmer Biomet is a leading global medical device company focusing on orthopaedics and sports medicine, with products covering artificial joint implants including femoral stems.
Features:
The company's technologically innovative and rigorously designed products enable it to offer several options to meet different patient needs, and it has an excellent reputation worldwide.
4.3. Oslo Technologies (Ottobock)
![奥斯陆科技 奥斯陆科技]()
Profile:
Oslo Technologies is a German company specialising in high quality orthopaedic implants and assistive devices, offering artificial hip solutions including femoral stems.
Features:
High-quality materials and designs, commitment to product innovation and improvement for a wide range of clinical conditions.
4.4.South East Medical (Smith & Nephew)
![东南医疗 东南医疗]()
Profile:
Southeast Medical is a well-known international medical device company specialising in orthopaedic implants and surgical tools, with its artificial hip joint products used worldwide.
Features:
It has a high reputation in the field of artificial joint implantation, and its product design focuses on long-term patient recovery and mobility.
4.5.meditech(Czmeditech)
![迈玛瑞 迈玛瑞]()
Profile:
Czmeditech is an orthopaedic-focused medical device and implant manufacturer with a strong commitment to providing high-quality, innovative orthopaedic implant solutions, with a particular focus on artificial hip and knee joints. Maimaritech supplies implants and assistive devices to hospitals and orthopaedic surgeons in several regions of the world
Features:
Commonly used in artificial hip replacement surgery, femoral stems manufactured by McMurry are made of high-strength, corrosion-resistant materials such as titanium and cobalt-chromium alloys to ensure their stability and durability. The femoral stem is designed in various forms to suit different patients' anatomy and surgical needs.
Conclusion
With over 20 years of experience, cutting-edge technology, and a commitment to quality and compliance, CZMEDITECH stands as a trusted partner for healthcare providers worldwide. Our maxillofacial steel plate implants are among the highest quality in the market, offering durability, precision, and value to our clients.
Whether you're a hospital, clinic, or surgeon, we provide the reliable and cost-effective solutions needed to deliver the best care to your patients.
English
Français
Русский
Español
العربية
Português
Deutsch
italiano
日本語
한국어
Nederlands
Tiếng Việt
ไทย
Polski
Türkçe
አማርኛ
ພາສາລາວ
ភាសាខ្មែរ
Bahasa Melayu
ဗမာစာ
தமிழ்
Filipino
Bahasa Indonesia
magyar
Română
Čeština
Монгол
қазақ
Српски
हिन्दी
فارسی
Kiswahili
Slovenčina
Slovenščina
Norsk
Svenska
українська
Ελληνικά
Suomi
Հայերեն
עברית
Latine
Dansk
اردو
Shqip
বাংলা
Hrvatski
Afrikaans
Gaeilge
Eesti keel
Māori
नेपाली
Oʻzbekcha
latviešu
অসমীয়া
Aymara
Azərbaycan dili
Bamanankan
Euskara
Беларуская мова
भोजपुरी
Bosanski
Български
Català
Cebuano
Corsu
ދިވެހި
डोग्रिड ने दी
Esperanto
Eʋegbe
Frysk
Galego
ქართული
guarani
ગુજરાતી
Kreyòl ayisyen
Hausa
ʻŌlelo Hawaiʻi
Hmoob
íslenska
Igbo
Ilocano
Basa Jawa
ಕನ್ನಡ
Kinyarwanda
गोंगेन हें नांव
Krio we dɛn kɔl Krio
Kurdî
Kurdî
Кыргызча
Lingala
Lietuvių
Oluganda
Lëtzebuergesch
Македонски
मैथिली
Malagasy
മലയാളം
Malti
मराठी
ꯃꯦꯇꯥꯏ (ꯃꯅꯤꯄꯨꯔꯤ) ꯴.
Mizo tawng
Chichewa
ଓଡ଼ିଆ
Afaan Oromoo
پښتو
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ
Runasimi
Gagana Samoa
संस्कृत
Gaelo Albannach
Sepeti
Sesotho
chiShona
سنڌي
Soomaali
Basa Sunda
Wikang Tagalog
Тоҷикӣ
Татарча
తెలుగు
ትግንያውያን
Xitsonga
Türkmençe
संस्कृत
ئۇيغۇرچە
Cymraeg
isiXhosa
ייִדיש
Yorùbá
isiZulu