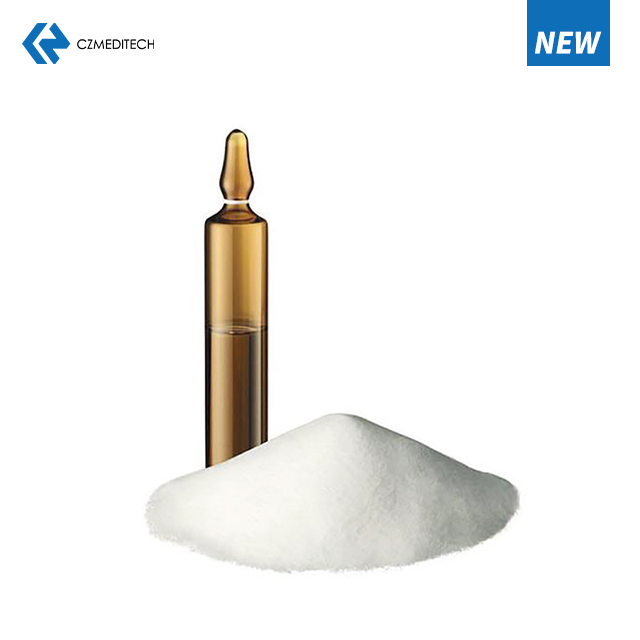
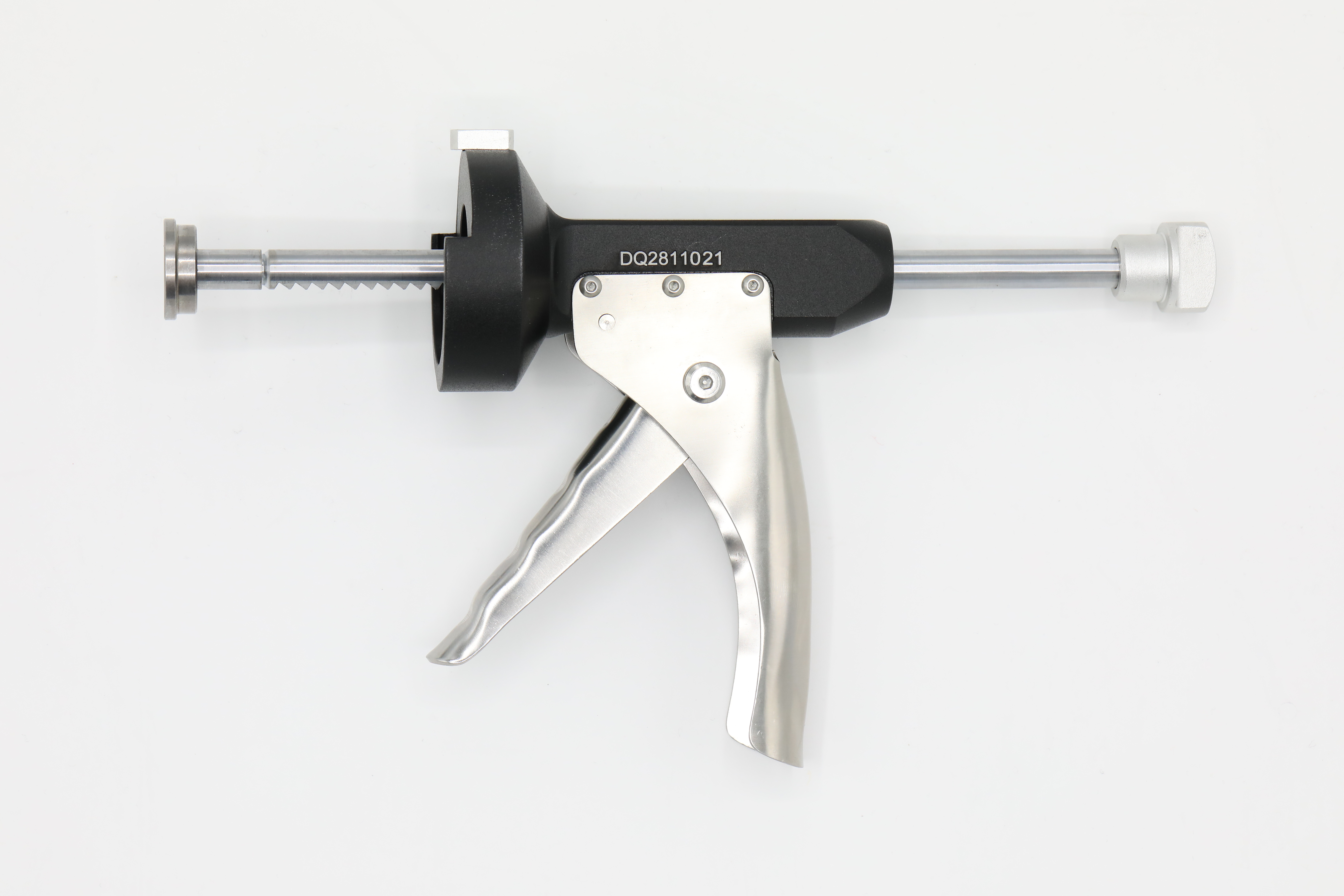
Joint bone cement is a polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA)–based orthopedic material designed to provide immediate and durable fixation between prosthetic implants and bone during joint replacement procedures. It plays a critical role in cemented hip and knee arthroplasty by ensuring mechanical stability, load transfer, and long-term implant performance.
CZMEDITECH provides high-quality joint bone cement solutions developed for modern orthopedic surgery, combining reliable handling characteristics, mechanical strength, and regulatory compliance for global markets.
What Is Joint Bone Cement in Orthopedic Surgery
Joint bone cement is a non-biological fixation material used to anchor orthopedic implants to bone surfaces during joint reconstruction procedures. Unlike biological bone bonding, bone cement achieves fixation through mechanical interlock with cancellous bone, allowing for immediate implant stability after surgery.
PMMA-based bone cement has been widely adopted in orthopedic practice due to its predictable performance, intraoperative controllability, and long clinical history in joint arthroplasty.
PMMA Bone Cement Composition and Working Principle
PMMA bone cement is supplied as a two-component system consisting of a powder and a liquid monomer. When mixed, the components undergo polymerization, transitioning from a dough-like state to a hardened structure.
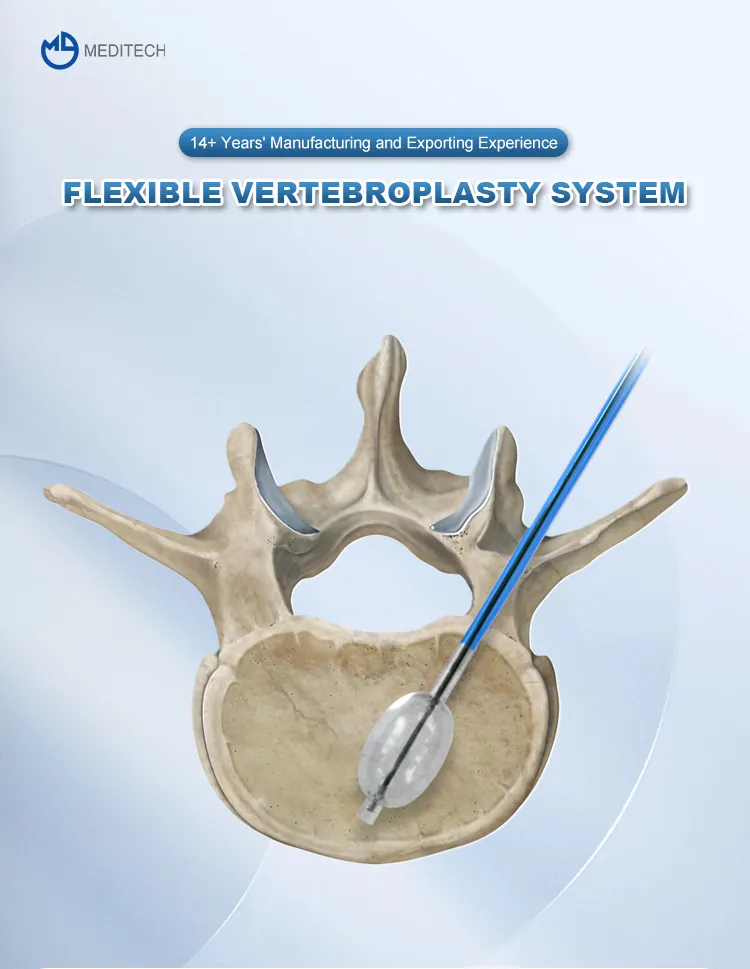
During this process, the cement penetrates cancellous bone surfaces and creates a mechanical interface that securely fixes the prosthesis in place. The fixation relies on mechanical stability rather than biological fusion, making it particularly suitable for cases requiring immediate load-bearing support.
Clinical Applications of Joint Bone Cement
Joint bone cement is primarily used in load-bearing orthopedic procedures where stable and long-lasting fixation is required. It is commonly applied in both primary joint replacement and revision surgery.
Bone Cement for Hip Arthroplasty and Knee Replacement
In total hip arthroplasty (THA) and total knee arthroplasty (TKA), bone cement is used to secure femoral stems, tibial components, and acetabular cups. Cemented fixation allows for precise implant positioning and consistent load distribution, particularly in patients with compromised bone quality.
Bone cement is frequently selected for elderly patients, osteoporotic bone conditions, and clinical scenarios where immediate post-operative stability is essential.
Cemented Fixation in Primary and Revision Joint Surgery
Cemented fixation remains an effective solution in revision joint surgery, where bone defects, altered anatomy, or reduced bone stock may limit the effectiveness of cementless implants. Bone cement enables surgeons to compensate for irregular bone surfaces and restore stable implant fixation in complex revision cases.
Key Features of CZMEDITECH Joint Bone Cement
CZMEDITECH joint bone cement is engineered to meet the clinical demands of orthopedic surgeons while supporting consistent manufacturing quality and international regulatory standards.
Optimized Viscosity and Controlled Polymerization Time
The cement formulation offers optimized viscosity to support easy handling during mixing and application. Controlled polymerization time allows surgeons adequate working time for accurate implant placement while ensuring reliable setting characteristics during surgery.
This balance between workability and setting time contributes to procedural efficiency and surgical precision.
High Mechanical Strength and Long-Term Fixation Stability
Designed to withstand repetitive joint loading, the cement demonstrates high mechanical strength and resistance to fatigue. Once cured, it provides durable fixation capable of supporting long-term physiological stresses associated with daily joint movement.
This mechanical reliability is essential for maintaining implant stability throughout the service life of joint prostheses.
Optional Antibiotic-Loaded Bone Cement Solutions
Antibiotic-loaded bone cement options are available to help reduce the risk of post-operative infection in high-risk patients or revision procedures. These formulations allow localized antibiotic delivery at the surgical site while maintaining essential mechanical performance.
Such solutions are commonly used in joint revision surgery and infection-sensitive clinical scenarios.
Indications and Surgical Compatibility
Joint bone cement is indicated for a wide range of orthopedic joint reconstruction procedures where cemented fixation is clinically appropriate.
Compatibility with Cemented Hip and Knee Prosthesis Systems
The cement is compatible with most cemented hip and knee prosthesis systems used in contemporary orthopedic practice. It supports standardized cementing techniques and integrates smoothly into established surgical workflows.
Quality Standards and Regulatory Compliance
CZMEDITECH joint bone cement is manufactured under a comprehensive quality management system designed to meet international medical device regulations.
CE Marking and ISO-Certified Manufacturing
Production is conducted in ISO-certified facilities, and the product complies with relevant CE medical device requirements. Strict process controls ensure batch-to-batch consistency, traceability, and regulatory readiness for international markets.
Biocompatibility and Safety Testing
All materials undergo biocompatibility and safety evaluations to ensure suitability for clinical use. Testing is performed to confirm compliance with applicable standards for orthopedic implant-related materials, supporting patient safety and clinical reliability.
OEM and Private Label Joint Bone Cement Solutions
CZMEDITECH offers OEM and private label joint bone cement services for distributors, orthopedic brands, and medical device companies worldwide. Flexible cooperation models support customized packaging, branding, and regulatory documentation according to regional market requirements.
Why Choose CZMEDITECH as Your Joint Bone Cement Manufacturer
With integrated manufacturing capabilities, regulatory experience, and global export support, CZMEDITECH serves as a reliable partner for orthopedic bone cement supply. Our focus on product consistency, compliance, and long-term cooperation enables distributors and healthcare providers to source joint bone cement solutions with confidence.
![Bone Cement]()
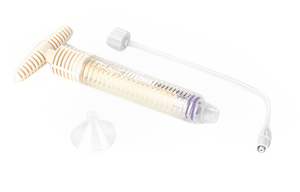
Heraeus trauma bone cement, imported from Germany. Stable quality and good in the surgery.
![Bone Cement]()
Powder and liquid mixed with antibiotic.
![Bone Cement]()
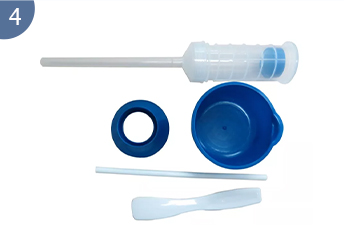
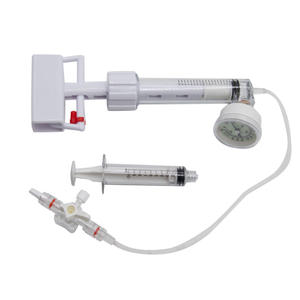
Bone cement injection easy to use and inject the bone cement to the fracture part.
![Bone Cement]()
Bone cement application kit disposable.
English
Français
Русский
Español
العربية
Português
Deutsch
italiano
日本語
한국어
Nederlands
Tiếng Việt
ไทย
Polski
Türkçe
አማርኛ
ພາສາລາວ
ភាសាខ្មែរ
Bahasa Melayu
ဗမာစာ
தமிழ்
Filipino
Bahasa Indonesia
magyar
Română
Čeština
Монгол
қазақ
Српски
हिन्दी
فارسی
Kiswahili
Slovenčina
Slovenščina
Norsk
Svenska
українська
Ελληνικά
Suomi
Հայերեն
עברית
Latine
Dansk
اردو
Shqip
বাংলা
Hrvatski
Afrikaans
Gaeilge
Eesti keel
Māori
नेपाली
Oʻzbekcha
latviešu
অসমীয়া
Aymara
Azərbaycan dili
Bamanankan
Euskara
Беларуская мова
भोजपुरी
Bosanski
Български
Català
Cebuano
Corsu
ދިވެހި
डोग्रिड ने दी
Esperanto
Eʋegbe
Frysk
Galego
ქართული
guarani
ગુજરાતી
Kreyòl ayisyen
Hausa
ʻŌlelo Hawaiʻi
Hmoob
íslenska
Igbo
Ilocano
Basa Jawa
ಕನ್ನಡ
Kinyarwanda
गोंगेन हें नांव
Krio we dɛn kɔl Krio
Kurdî
Kurdî
Кыргызча
Lingala
Lietuvių
Oluganda
Lëtzebuergesch
Македонски
मैथिली
Malagasy
മലയാളം
Malti
मराठी
ꯃꯦꯇꯥꯏ (ꯃꯅꯤꯄꯨꯔꯤ) ꯴.
Mizo tawng
Chichewa
ଓଡ଼ିଆ
Afaan Oromoo
پښتو
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ
Runasimi
Gagana Samoa
संस्कृत
Gaelo Albannach
Sepeti
Sesotho
chiShona
سنڌي
Soomaali
Basa Sunda
Wikang Tagalog
Тоҷикӣ
Татарча
తెలుగు
ትግንያውያን
Xitsonga
Türkmençe
संस्कृत
ئۇيغۇرچە
Cymraeg
isiXhosa
ייִדיש
Yorùbá
isiZulu