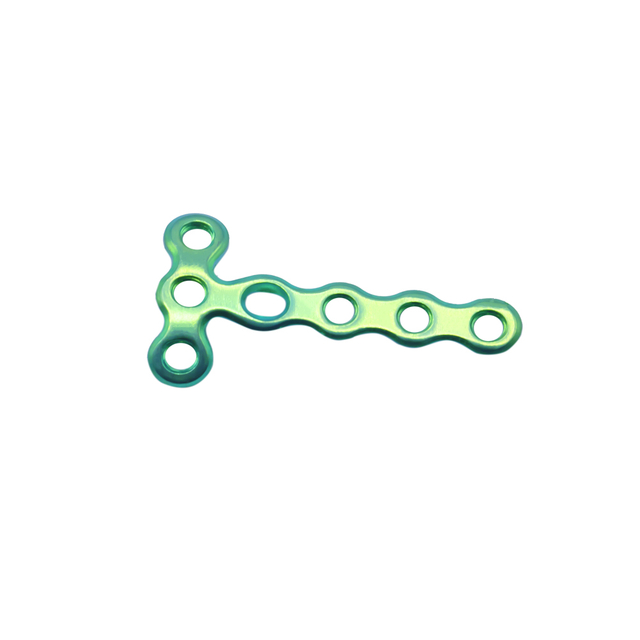
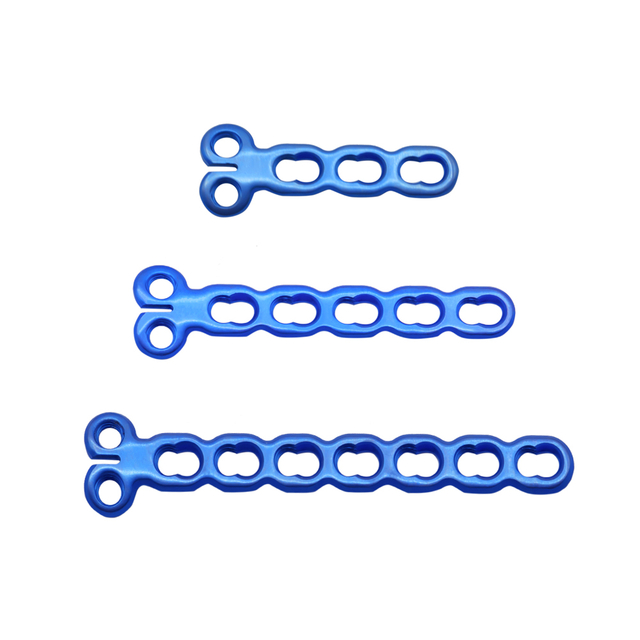
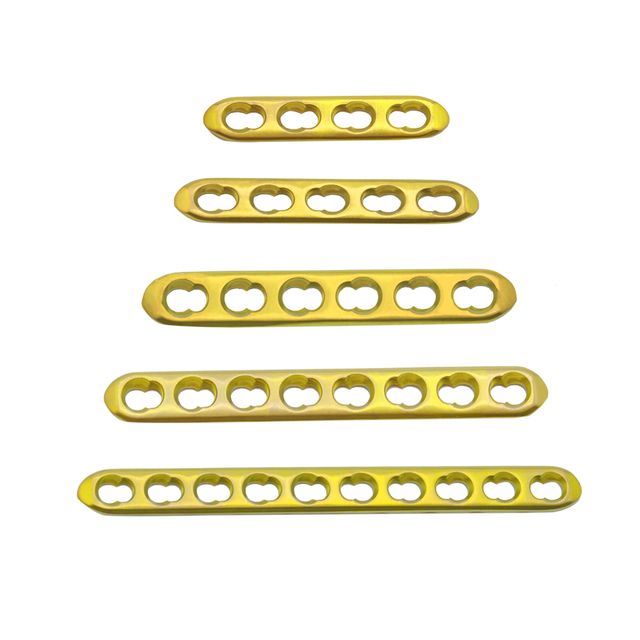
What is mini fragment?
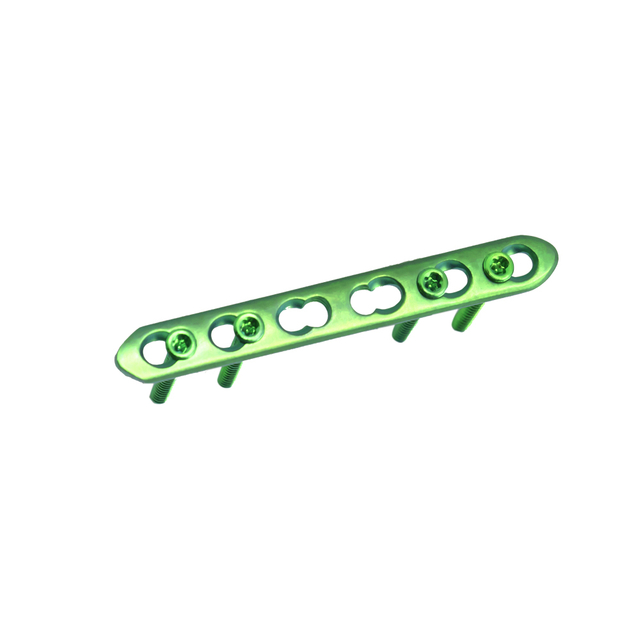
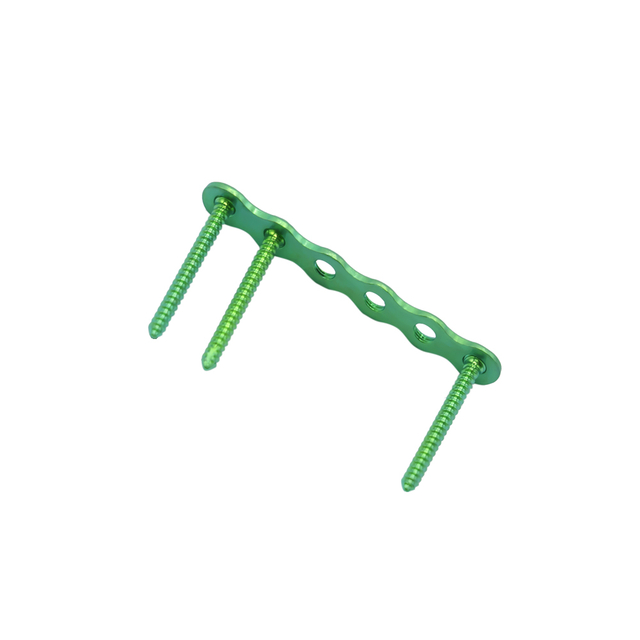
Mini fragment refers to a type of orthopedic implant used to fix small bones and bone fragments, typically those measuring 2.0 to 3.5 mm in diameter. These implants are commonly used in hand and foot surgeries, as well as other surgeries that involve small bone fragments. Mini fragment implants are designed to provide stable fixation and promote healing, and are available in various shapes and sizes to accommodate different surgical needs. They are typically made of biocompatible materials such as titanium or stainless steel, and are usually inserted using specialized instruments.
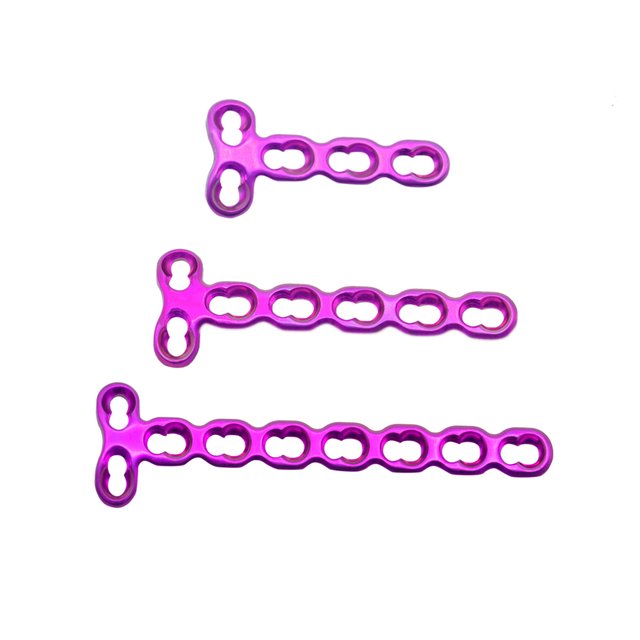
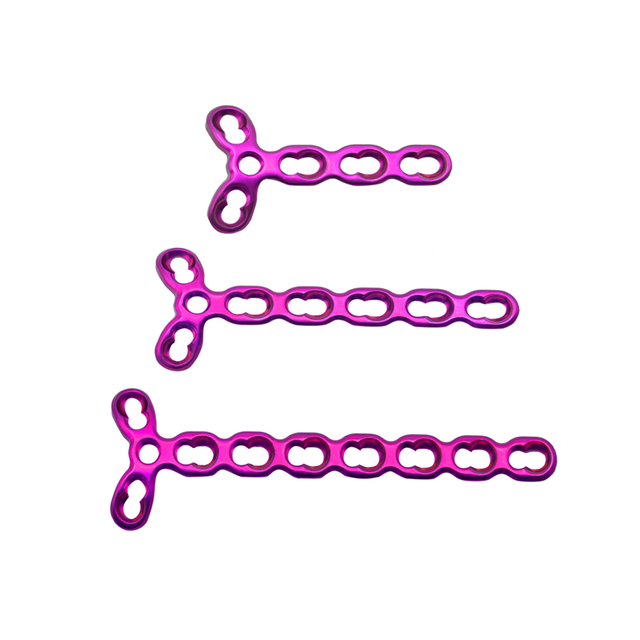
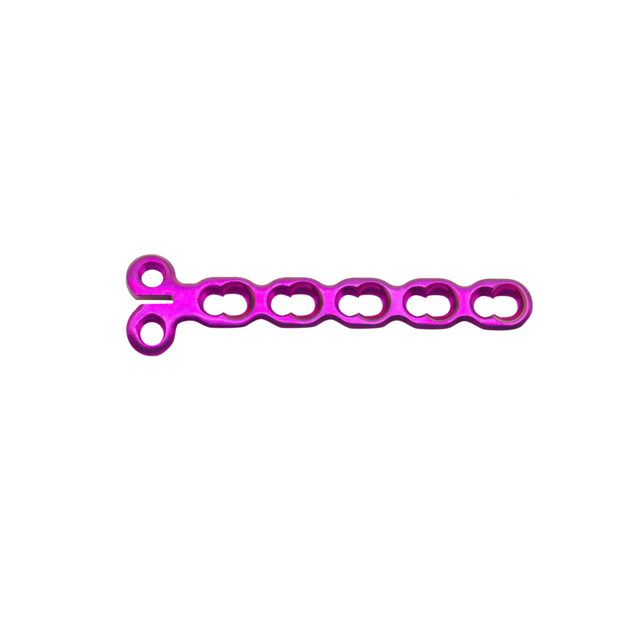
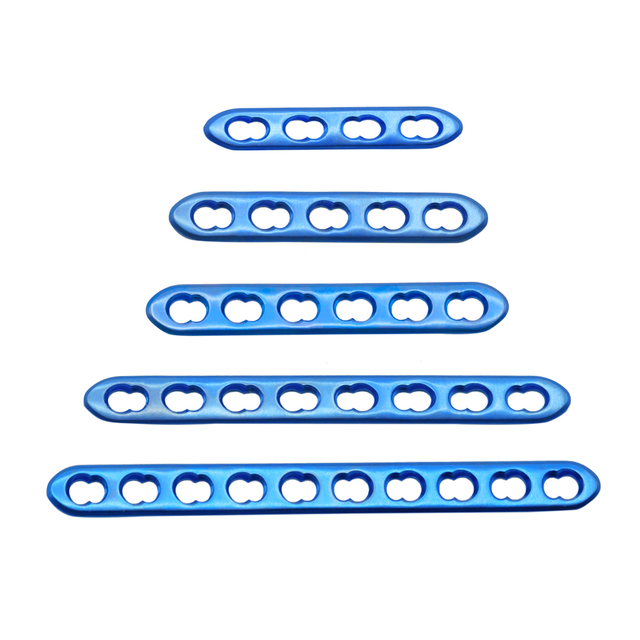
What are the types of mini fragment?
Mini fragment plates are available in various types and sizes to fit different anatomical locations and bone sizes. Some common types of mini fragment plates include:
One-third tubular plates: These are used for small bone fragments or small bone fragments with limited space for fixation, such as in the hand, wrist, and ankle.
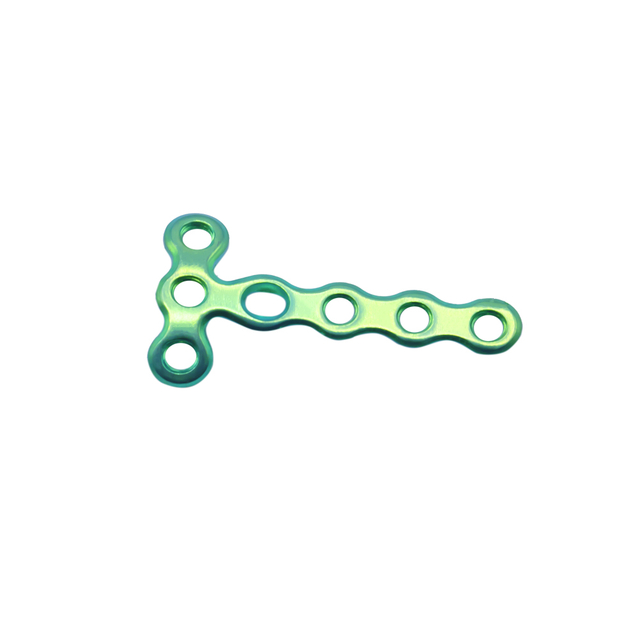
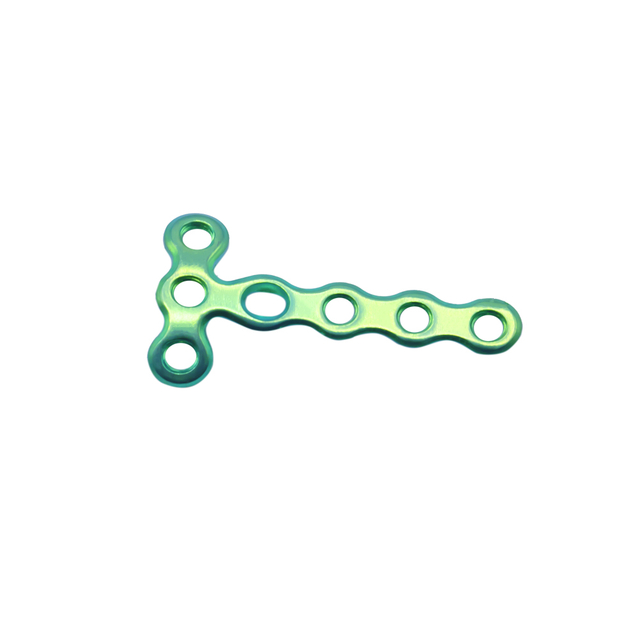
T-plates: These plates are commonly used in fractures of the distal radius, ankle, and calcaneus.
L-plates: These plates are used in fractures that require fixation perpendicular to the long axis of the bone, such as in distal femoral fractures.
H-plates: These plates are used in fractures of the proximal tibia, as well as in the treatment of non-unions.
Y-plates: These plates are used for fractures of the proximal humerus, clavicle, and distal femur.
Hook plates: These plates are used in complex fractures where conventional plating techniques are not feasible or have failed, such as in fractures of the lateral tibial plateau.
It is important to note that the types and sizes of mini fragment plates used will depend on the specific fracture pattern and the surgeon's preference.
Materials of the locking plate?
Locking plates are typically made of biocompatible materials such as titanium, titanium alloy, or stainless steel. These materials have excellent strength, stiffness, and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for use in orthopedic implants. In addition, they are inert and do not react with body tissues, reducing the risk of rejection or inflammation. Some locking plates may also be coated with materials such as hydroxyapatite or other coatings to improve their integration with bone tissue.
Which plate is better titanium or stainless steel?
Both titanium and stainless steel plates are commonly used in orthopedic surgeries, including for locking plates. The choice between the two materials depends on several factors, including the type of surgery, the patient's medical history and preferences, and the surgeon's experience and preference.
Titanium is a lightweight and strong material that is biocompatible and resistant to corrosion, making it an excellent choice for medical implants. Titanium plates are less stiff than stainless steel plates, which can help reduce stress on the bone and promote healing. Additionally, titanium plates are more radiolucent, which means they do not interfere with imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI.
Stainless steel, on the other hand, is a stronger and stiffer material that is also biocompatible and resistant to corrosion. It has been used in orthopedic implants for decades and is a tried-and-true material. Stainless steel plates are less expensive than titanium plates, which can be a consideration for some patients.
Why titanium plates are used in surgery?
Titanium plates are often used in surgery because of their unique properties that make them an ideal material for medical implants. Some of the benefits of using titanium plates in surgery include:
Biocompatibility: Titanium is highly biocompatible, which means that it is unlikely to cause an allergic reaction or be rejected by the body's immune system. This makes it a safe and reliable material for use in medical implants.
Strength and durability: Titanium is one of the strongest and most durable metals, which makes it an ideal material for implants that need to withstand the stresses and strains of everyday use.
Corrosion resistance: Titanium is highly resistant to corrosion and is less likely to react with bodily fluids or other materials in the body. This helps to prevent the implant from corroding or degrading over time.
Radiopacity: Titanium is highly radiopaque, which means that it can be easily seen on X-rays and other imaging tests. This makes it easier for doctors to monitor the implant and ensure that it is functioning properly.
සිංහල
English
Français
Русский
Español
العربية
Português
Deutsch
italiano
한국어
Tiếng Việt
ไทย
Polski
Türkçe
ພາສາລາວ
ភាសាខ្មែរ
Bahasa Melayu
ဗမာစာ
Filipino
Bahasa Indonesia
magyar
Română
Čeština
Монгол
қазақ
Српски
हिन्दी
فارسی
Kiswahili
Slovenčina
Slovenščina
українська
Ελληνικά
Latine
বাংলা
Afrikaans
Māori
नेपाली
Oʻzbekcha
latviešu
Azərbaycan dili
Беларуская мова
Български
Esperanto
ქართული
Kreyòl ayisyen
Kinyarwanda
Кыргызча
Lietuvių
Lëtzebuergesch
Malti
संस्कृत
Soomaali
Türkmençe
ئۇيغۇرچە