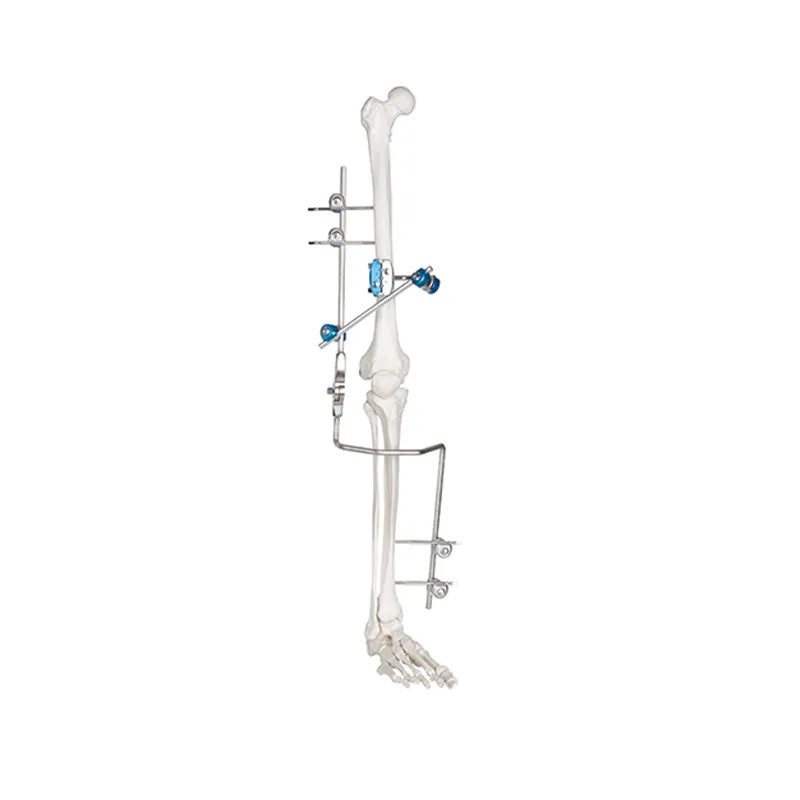
Knee Joint External Fixator: An Overview
The knee joint is one of the most complex joints in the human body. It is the largest joint and connects the thigh bone (femur) to the shin bone (tibia). Injuries to the knee joint are common and can range from minor sprains to severe ligament tears or fractures. In some cases, surgery is required to stabilize the knee joint and promote healing. One of the surgical techniques used to treat knee joint injuries is the external fixation method. This article will provide an overview of knee joint external fixators, including their types, indications, and benefits.
What is a Knee Joint External Fixator?
A knee joint external fixator is a surgical device used to stabilize the knee joint and promote healing after an injury or surgery. It is an external device that is fixed to the bone with pins or wires and connected with rods or struts. The fixator holds the bones in the correct position, allowing them to heal properly.
Types of Knee Joint External Fixators
There are two types of knee joint external fixators:
Circular External Fixator
A circular external fixator consists of rings that are attached to the bone with wires or pins. The rings are connected with rods or struts, forming a circular frame around the limb. The frame can be adjusted to control the position of the bones and to allow movement of the joint.
Unilateral External Fixator
A unilateral external fixator is a device that is fixed to one side of the bone with pins or screws. The other side of the bone is not fixed, allowing for controlled movement of the joint. This type of fixator is less invasive than the circular fixator and is often used for less severe injuries.
Indications for Knee Joint External Fixation
Knee joint external fixation is indicated for a variety of injuries and conditions, including:
Fractures
Knee joint fractures can be treated with external fixation. The fixator holds the bones in the correct position while they heal.
Dislocations
Knee joint dislocations can also be treated with external fixation. The fixator holds the bones in the correct position while the ligaments and tendons heal.
Ligament Injuries
Ligament injuries, such as anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears, can be treated with external fixation. The fixator holds the bones in the correct position while the ligament heals.
Osteotomies
Osteotomies, which are surgical procedures that involve cutting and reshaping bones, can be treated with external fixation. The fixator holds the bones in the correct position while they heal.
Infections
In some cases, knee joint infections can be treated with external fixation. The fixator allows for proper drainage of the infection and prevents further damage to the joint.
Benefits of Knee Joint External Fixation
Knee joint external fixation offers several benefits over other surgical techniques, including:
Minimally Invasive
External fixation is a minimally invasive technique that does not require large incisions or extensive dissection of the tissues.
Customizable
External fixation devices can be customized to fit the patient's specific injury and anatomy.
Adjustable
External fixation devices can be adjusted to control the position of the bones and to allow for controlled movement of the joint.
Early Mobilization
External fixation allows for early mobilization of the joint, which can promote faster healing and prevent joint stiffness.
Reduced Risk of Complications
External fixation has a lower risk of complications compared to other surgical techniques.
Conclusion
Knee joint external fixation is a valuable surgical technique used to stabilize the knee joint and promote healing after an injury or surgery. It offers several benefits over other surgical techniques, including minimally invasive surgery, early mobil ization of the joint, and reduced risk of complications. There are two types of external fixators used for knee joint injuries: circular external fixator and unilateral external fixator. Indications for knee joint external fixation include fractures, dislocations, ligament injuries, osteotomies, and infections.
In conclusion, knee joint external fixation is an effective surgical technique for treating knee joint injuries. It allows for proper healing and promotes early mobilization of the joint, leading to faster recovery and reduced risk of complications. If you are suffering from a knee joint injury, it is important to discuss your treatment options with a qualified healthcare provider to determine if knee joint external fixation is right for you.
FAQs
Is knee joint external fixation painful?
Ans: Patients may experience some discomfort after surgery, but pain can be managed with medications prescribed by the healthcare provider.
How long does it take to recover from knee joint external fixation surgery?
Ans: Recovery time varies depending on the severity of the injury and the patient's overall health. It may take several weeks or months to fully recover.
Can knee joint external fixation be used for all types of knee joint injuries?
Ans: No, knee joint external fixation is indicated for specific types of injuries and conditions, as determined by the healthcare provider.
Are there any risks associated with knee joint external fixation surgery?
Ans: As with any surgical procedure, there are risks associated with knee joint external fixation surgery, including infection, nerve damage, and blood clots.
How long is the external fixator worn after knee joint surgery?
Ans: The length of time the external fixator is worn varies depending on the severity of the injury and the patient's recovery progress. Your healthcare provider will determine when the fixator can be removed.
English
Français
Русский
Español
العربية
Português
Deutsch
italiano
日本語
한국어
Nederlands
Tiếng Việt
ไทย
Polski
Türkçe
አማርኛ
ພາສາລາວ
ភាសាខ្មែរ
Bahasa Melayu
ဗမာစာ
தமிழ்
Filipino
Bahasa Indonesia
magyar
Română
Čeština
Монгол
қазақ
Српски
हिन्दी
فارسی
Kiswahili
Slovenčina
Slovenščina
Norsk
Svenska
українська
Ελληνικά
Suomi
Հայերեն
עברית
Latine
Dansk
اردو
Shqip
বাংলা
Hrvatski
Afrikaans
Gaeilge
Eesti keel
Māori
नेपाली
Oʻzbekcha
latviešu
অসমীয়া
Aymara
Azərbaycan dili
Bamanankan
Euskara
Беларуская мова
भोजपुरी
Bosanski
Български
Català
Cebuano
Corsu
ދިވެހި
डोग्रिड ने दी
Esperanto
Eʋegbe
Frysk
Galego
ქართული
guarani
ગુજરાતી
Kreyòl ayisyen
Hausa
ʻŌlelo Hawaiʻi
Hmoob
íslenska
Igbo
Ilocano
Basa Jawa
ಕನ್ನಡ
Kinyarwanda
गोंगेन हें नांव
Krio we dɛn kɔl Krio
Kurdî
Kurdî
Кыргызча
Lingala
Lietuvių
Oluganda
Lëtzebuergesch
Македонски
मैथिली
Malagasy
മലയാളം
Malti
मराठी
ꯃꯦꯇꯥꯏ (ꯃꯅꯤꯄꯨꯔꯤ) ꯴.
Mizo tawng
Chichewa
ଓଡ଼ିଆ
Afaan Oromoo
پښتو
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ
Runasimi
Gagana Samoa
संस्कृत
Gaelo Albannach
Sepeti
Sesotho
chiShona
سنڌي
Soomaali
Basa Sunda
Wikang Tagalog
Тоҷикӣ
Татарча
తెలుగు
ትግንያውያን
Xitsonga
Türkmençe
संस्कृत
ئۇيغۇرچە
Cymraeg
isiXhosa
ייִדיש
Yorùbá
isiZulu