Introduction
Fractures can significantly impact a person's quality of life, requiring effective methods of treatment to facilitate proper healing. In recent years, advancements in orthopedic technology have revolutionized fracture fixation procedures. One such innovation is the locking plate, which has gained popularity among surgeons and patients alike due to its superior biomechanical properties and improved patient outcomes. This article explores the concept of locking plates, their benefits, and future developments in the field.
A locking plate is a specialized implant used in orthopedic surgery to stabilize and promote the healing of fractures. It consists of a metal plate with multiple threaded holes and scre
ws that lock into these holes, providing a rigid fixation. Unlike traditional plates, which rely on friction between the plate and bone, locking plates achieve stability by locking the screws to the plate, forming a fixed-angle construct.
Locking plates utilize a unique screw-plate interface that enables the screws to lock into the plate, creating a stable construct. This construct distributes the load more evenly along the bone, reducing stress concentration and minimizing the risk of implant failure. The locking mechanism also prevents the screws from loosening over time, enhancing the long-term stability of the fracture fixation.
![Locking Plate]()
Benefits of Locking Plates in Fracture Fixation
Increased Stability
The locking mechanism of plates offers increased stability compared to traditional plating systems. The fixed-angle construct minimizes micromotion at the fracture site, promoting primary bone healing and reducing the risk of secondary displacement. This enhanced stability allows for early mobilization and accelerates the rehabilitation process.
Improved Healing Process
Locking plates provide excellent support for fracture fragments, promoting the healing process. The rigid fixation minimizes the need for external supports such as casts or braces, allowing patients to regain functional mobility sooner. Additionally, the direct compression achieved by locking plates stimulates callus formation and accelerates bone union.
Reduced Risk of Infection
The design of locking plates reduces the risk of infection. The locking screws create a more secure fixation, preventing the accumulation of bacteria in the gap between.
The plate and bone. Moreover, the decreased reliance on compression reduces the likelihood of soft tissue compromise, lowering the risk of infection even further.
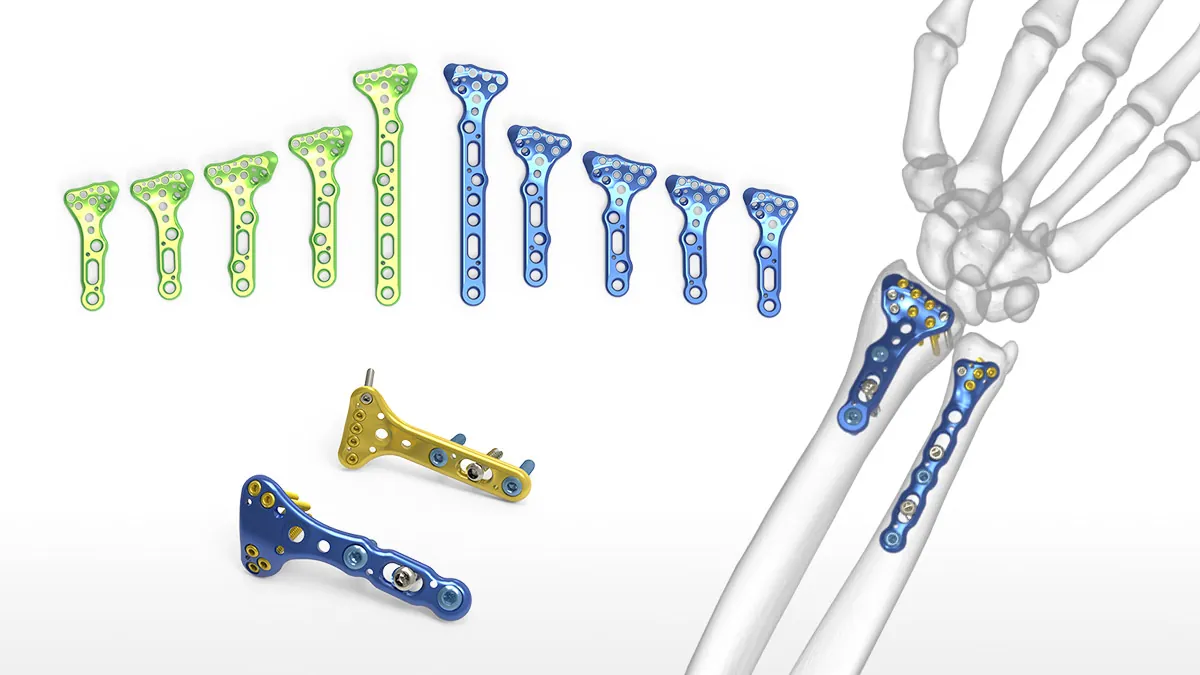
Versatility in Fixation
Locking plates offer versatility in fracture fixation. They can be used for various types of fractures, including complex and comminuted fractures, where traditional plating methods may be less effective. The ability to choose screw trajectories independently of the plate position allows surgeons to tailor the fixation to the specific needs of each patient.
Locking plates are available in different configurations to accommodate the anatomical variations and fracture patterns encountered in clinical practice. The common types include:
1. Straight Locking Plates: Used for fractures in long bones, such as the femur or humerus.
2. L-shaped Locking Plates: Suitable for fractures involving joint surfaces.
3. T-shaped Locking Plates: Used for fractures at the metaphysis or diaphysis.
4. Curved Locking Plates: Designed for fractures in curved bones, such as the clavicle or scapula.
Each type of locking plate is designed to address specific fracture patterns and provide optimal stability.
![Locking Plate Type]()
Surgical Procedure for Locking Plate Fixation
The surgical procedure for locking plate fixation involves several key steps:
1. Preoperative planning: Surgeons evaluate the fracture type, select the appropriate locking plate, and determine the screw trajectories.
2. Incision and exposure: A carefully planned incision is made over the fracture site to provide access for plate placement.
3. Reduction and fixation: Fracture fragments are realigned and held in place using temporary fixation methods, such as K-wires or clamps. The locking plate is then positioned and fixed to the bone using locking screws.
4. Closure and rehabilitation: Once the plate is securely fixed, the incision is closed, and the patient undergoes a tailored rehabilitation program to regain strength and mobility.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Following locking plate fixation, patients undergo a structured rehabilitation program that focuses on early mobilization and functional restoration. The program typically includes exercises to improve range of motion, muscle strength, and joint stability. Physical therapy plays a crucial role in optimizing the healing process and facilitating the return to normal activities.
Potential Complications
While locking plates have shown significant advantages in fracture fixation, there are potential complications that can arise:
Implant Failure
In rare cases, the locking plate or screws may fail due to factors such as implant fatigue, improper positioning, or excessive loading. Regular follow-up visits with the orthopedic surgeon are essential to monitor the implant's integrity and detect any signs of failure.
Infection
Although the risk of infection is relatively low with locking plates, it is still a possible complication. Close adherence to sterile surgical techniques, appropriate antibiotic prophylaxis, and careful postoperative wound care can help minimize the risk of infection.
Nonunion or Delayed Union
In some instances, fractures may not heal properly, resulting in nonunion or delayed union. Factors that can contribute to this include poor blood supply, inadequate immobilization, or patient-related factors such as smoking or nutritional deficiencies. Additional interventions, such as bone grafting or revision surgery, may be necessary to promote bone healing.
Future Developments in Locking Plate Technology
Locking plate technology continues to evolve, with ongoing research focused on further improving fracture fixation outcomes. Some areas of development include:
1. Biodegradable Locking Plates: These plates are designed to degrade over time, reducing the need for plate removal surgeries.
2. Advanced Materials: The exploration of new materials, such as bioactive coatings or composite materials, aims to enhance bone integration and reduce complications.
3. Patient-Specific Locking Plates: Utilizing advanced imaging techniques, locking plates can be custom-designed to fit an individual patient's anatomy,
optimizing fixation and reducing the risk of complications.
As research and technological advancements progress, the future holds great promise for further enhancing the efficacy and safety of locking plates in fracture fixation.
Conclusion
Locking plates have revolutionized fracture fixation, offering increased stability, improved healing, and reduced complications compared to traditional plating methods. These advanced implants provide versatile options for various fracture patterns and allow for early mobilization and accelerated rehabilitation. With ongoing advancements in locking plate technology, the future looks promising for even better patient outcomes and further refinement of fracture fixation techniques.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. How long does it take for a fracture fixed with a locking plate to heal?
- The healing time can vary depending on the specific fracture, patient factors, and other variables. Generally, it may take several weeks to months for the fracture to heal completely.
2. Are locking plates suitable for all types of fractures?
- Locking plates are suitable for a wide range of fractures, including complex and comminuted fractures. However, the suitability of a locking plate for a specific fracture is determined by the orthopedic surgeon based on several factors.
3. What is the difference between a locking plate and a traditional plate?
- The main difference lies in the fixation mechanism. Locking plates use screws that lock into the plate, creating a fixed-angle construct, while traditional plates rely on friction between the plate and bone for stability.
4. Can locking plates be removed after the fracture heals?
- In many cases, locking plates do not require removal unless they cause discomfort or other complications. The decision for plate removal is made by the orthopedic surgeon based on individual patient needs.
5. Is the surgical procedure for locking plate fixation complex?
- The surgical procedure for locking plate fixation requires expertise and precision. It is typically performed by orthopedic surgeons who specialize in fracture fixation procedures and have extensive training in the technique.
How to Buy Orthopaedic Implants and Orthopaedic Instruments?
For CZMEDITECH, we have a very complete product line of orthopedic surgery implants and corresponding instruments, the products including spine implants, intramedullary nails, trauma plate, locking plate, cranial-maxillofacial, prosthesis, power tools, external fixators, arthroscopy, veterinary care and their supporting instrument sets.
In addition, we are committed to continuously developing new products and expanding product lines, so as to meet the surgical needs of more doctors and patients, and also make our company more competitive in the whole global orthopedic implants and instruments industry.
We export worldwide, so you can contact us at email address song@orthopedic-china.com for a free quote, or send a message on WhatsApp for a quick response +86-18112515727.
If want to know more information,click CZMEDITECH to find more details.
English
Français
Русский
Español
العربية
Português
Deutsch
italiano
日本語
한국어
Nederlands
Tiếng Việt
ไทย
Polski
Türkçe
አማርኛ
ພາສາລາວ
ភាសាខ្មែរ
Bahasa Melayu
ဗမာစာ
தமிழ்
Filipino
Bahasa Indonesia
magyar
Română
Čeština
Монгол
қазақ
Српски
हिन्दी
فارسی
Kiswahili
Slovenčina
Slovenščina
Norsk
Svenska
українська
Ελληνικά
Suomi
Հայերեն
עברית
Latine
Dansk
اردو
Shqip
বাংলা
Hrvatski
Afrikaans
Gaeilge
Eesti keel
Māori
नेपाली
Oʻzbekcha
latviešu
অসমীয়া
Aymara
Azərbaycan dili
Bamanankan
Euskara
Беларуская мова
भोजपुरी
Bosanski
Български
Català
Cebuano
Corsu
ދިވެހި
डोग्रिड ने दी
Esperanto
Eʋegbe
Frysk
Galego
ქართული
guarani
ગુજરાતી
Kreyòl ayisyen
Hausa
ʻŌlelo Hawaiʻi
Hmoob
íslenska
Igbo
Ilocano
Basa Jawa
ಕನ್ನಡ
Kinyarwanda
गोंगेन हें नांव
Krio we dɛn kɔl Krio
Kurdî
Kurdî
Кыргызча
Lingala
Lietuvių
Oluganda
Lëtzebuergesch
Македонски
मैथिली
Malagasy
മലയാളം
Malti
मराठी
ꯃꯦꯇꯥꯏ (ꯃꯅꯤꯄꯨꯔꯤ) ꯴.
Mizo tawng
Chichewa
ଓଡ଼ିଆ
Afaan Oromoo
پښتو
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ
Runasimi
Gagana Samoa
संस्कृत
Gaelo Albannach
Sepeti
Sesotho
chiShona
سنڌي
Soomaali
Basa Sunda
Wikang Tagalog
Тоҷикӣ
Татарча
తెలుగు
ትግንያውያን
Xitsonga
Türkmençe
संस्कृत
ئۇيغۇرچە
Cymraeg
isiXhosa
ייִדיש
Yorùbá
isiZulu













